BBC
BBCMidwife Siro Devi is clinging to Monica Thatte, sobbing. Monica, in her late 20s, has returned to her birthplace – the Indian town where Siro has delivered hundreds of babies.
But this is no straightforward reunion. There is a painful history behind Siro’s tears. Shortly before Monica was born, Siro and several Indian midwives like her were regularly pressured to murder newborn girls.
Monica, evidence suggests, is one they saved.
I have been following Siro’s story for 30 years, ever since I went to interview her and four other rural midwives in India’s Bihar state in 1996.
They had been identified by a non-governmental organisation as being behind the murder of baby girls in the district of Katihar where, under pressure from the newborns’ parents, they were killing them by feeding them chemicals or simply wringing their necks.
Hakiya Devi, the eldest of the midwives I interviewed, told me at the time she had killed 12 or 13 babies. Another midwife, Dharmi Devi, admitted to killing more – at least 15-20.
It is impossible to ascertain the exact number of babies they may have killed, given the way the data was gathered.
But they featured in a report published in 1995 by an NGO, based on interviews with them and 30 other midwives. If the report’s estimates are accurate, more than 1,000 baby girls were being murdered every year in one district, by just 35 midwives. According to the report, Bihar at the time had more than half a million midwives. And infanticide was not limited to Bihar.
Refusing orders, Hakiya said, was almost never an option for a midwife.
“The family would lock the room and stand behind us with sticks,” says Hakiya Devi. “They’d say: ‘We already have four-five daughters. This will wipe out our wealth. Once we give dowry for our girls, we will starve to death. Now, another girl has been born. Kill her.’
“Who could we complain to? We were scared. If we went to the police, we’d get into trouble. If we spoke up, people would threaten us.”

The role of a midwife in rural India is rooted in tradition, and burdened by the harsh realities of poverty and caste. The midwives I interviewed belonged to the lower castes in India’s caste hierarchy. Midwifery was a profession passed on to them by mothers and grandmothers. They lived in a world where refusing orders of powerful, upper-caste families was unthinkable.
The midwife could be promised a sari, a sack of grain or a small amount of money for killing a baby. Sometimes even that was not paid. The birth of a boy earned them about 1,000 rupees. The birth of a girl earned them half.
The reason for this imbalance was steeped in India’s custom of giving a dowry, they explained. Though the custom was outlawed in 1961, it still held strong in the 90s – and indeed continues into the present day.
A dowry can be anything – cash, jewellery, utensils. But for many families, rich or poor, it is the condition of a wedding. And this is what, for many, still makes the birth of a son a celebration and the birth of a daughter a financial burden.
Siro Devi, the only midwife of those I interviewed who is still alive, used a vivid physical image to explain this disparity in status.

“A boy is above the ground – higher. A daughter is below – lower. Whether a son feeds or takes care of his parents or not, they all want a boy.”
The preference for sons can be seen in India’s national-level data. Its most recent census, in 2011, recorded a ratio of 943 women to every 1,000 men. This is nevertheless an improvement on the 1990s – in the 1991 census, the ratio was 927/1,000.

By the time I finished filming the midwives’ testimonies in 1996, a small, silent change had begun. The midwives who once carried out these orders had started to resist.
This change was instigated by Anila Kumari, a social worker who supported women in the villages around Katihar, and was dedicated to addressing the root causes of these killings.
Anila’s approach was simple. She asked the midwives, “Would you do this to your own daughter?”
Her question apparently pierced years of rationalisation and denial. The midwives got some financial help via community groups and gradually the cycle of violence was interrupted.
Siro, speaking to me in 2007, explained the change.
“Now, whoever asks me to kill, I tell them: ‘Look, give me the child, and I’ll take her to Anila Madam.’”
The midwives rescued at least five newborn girls from families who wanted them killed or had already abandoned them.
One child died, but Anila arranged for the other four to be sent to Bihar’s capital, Patna, to an NGO which organised their adoption.
The story could have ended there. But I wanted to know what had become of those girls who were adopted, and where life had taken them.


Anila’s records were meticulous but they had few details about post-adoption.
Working with a BBC World Service team, I got in touch with a woman called Medha Shekar who, back in the 90s, was researching infanticide in Bihar when the babies rescued by Anila and the midwives began arriving at her NGO. Remarkably, Medha was still in touch with a young woman who, she believed, was one of these rescued babies.
Anila told me that she had given all the girls saved by the midwives the prefix “Kosi” before their name, a homage to the Kosi river in Bihar. Medha remembered that Monica had been named with this “Kosi” prefix before her adoption.
The adoption agency would not let us look at Monica’s records, so we can never be sure. But her origins in Patna, her approximate date of birth and the prefix “Kosi” all point to the same conclusion: Monica is, in all probability, one of the five babies rescued by Anila and the midwives.
When I went to meet her at her parents’ home some 2,000km (1,242 miles) away in Pune, she said she felt lucky to have been adopted by a loving family.

“This is my definition of a normal happy life and I am living it,” she said.
Monica knew that she had been adopted from Bihar. But we were able to give her more details about the circumstances of her adoption.
Earlier this year, Monica travelled to Bihar to meet Anila and Siro.
Monica saw herself as the culmination of years of hard work by Anila and the midwives.
“Someone prepares a lot to do well in an exam. I feel like that. They did the hard work and now they’re so curious to meet the result… So definitely, I would like to meet them.”

Anila wept tears of joy when she met Monica. But Siro’s response felt different.
She sobbed hard, holding Monica close and combing through her hair.
“I took you [to the orphanage] to save your life… My soul is at peace now,” she told her.
But when, a couple of days later, I attempted to press Siro about her reaction, she resisted further scrutiny.
“What happened in the past is in the past,” she said.
But what is not in the past is the prejudice some still hold against baby girls.
Reports of infanticide are now relatively rare, but sex-selective abortion remains common, despite being illegal since 1994.
If one listens to the traditional folk songs sung during childbirth, known as Sohar, in parts of north India, joy is reserved for the birth of a male child. Even in 2024, it is an effort to get local singers to change the lyrics so that the song celebrates the birth of a girl.
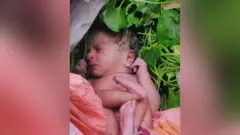
While we were filming our documentary, two baby girls were discovered abandoned in Katihar – one in bushes, another at the roadside, just a few hours old. One later died. The other was put up for adoption.

Before Monica left Bihar, she visited this baby in the Special Adoption Centre in Katihar.
She says she was haunted by the realisation that though female infanticide may have been reduced, abandoning baby girls continues.
“This is a cycle… I can see myself there a few years ago, and now again there’s some girl similar to me.”
But there were to be happier similarities too.
The baby has now been adopted by a couple in the north-eastern state of Assam. They have named her Edha, which means happiness.

“We saw her photo, and we were clear – a baby once abandoned cannot be abandoned twice,” says her adoptive father Gaurav, an officer in the Indian air force.
Every few weeks Gaurav sends me a video of Edha’s latest antics. I sometimes share them with Monica.
Looking back, the 30 years spent on this story were never just about the past. It was about confronting uncomfortable truths. The past cannot be undone, but it can be transformed.
And in that transformation, there is hope.