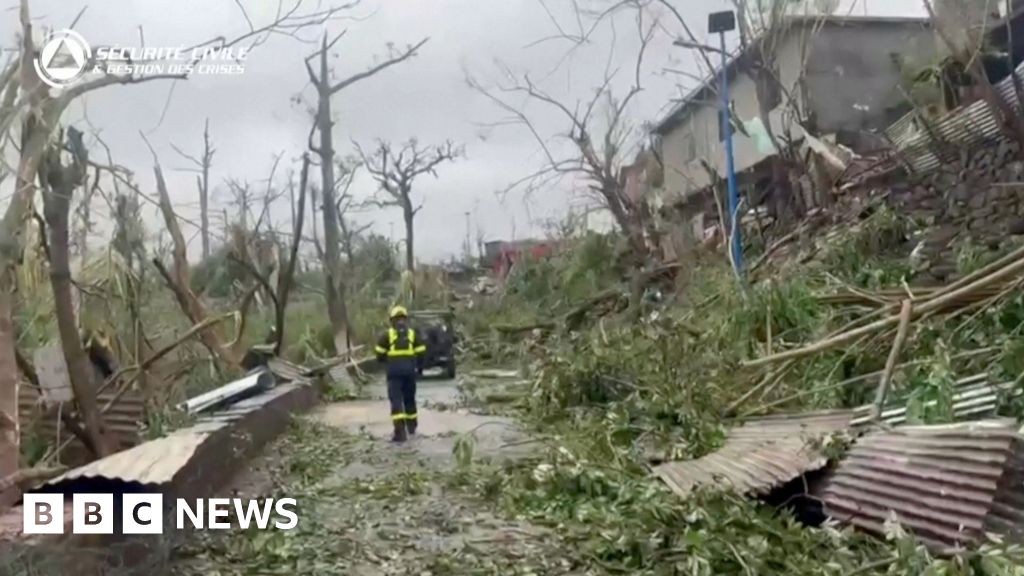
Residents of Maoytte have spoken of “apocalyptic scenes” caused by by the worst storm in 90 years to hit the French Indian Ocean territory.
Cyclone Chido brought wind speeds of more than 225km/h (140mph), flattening areas where the poorest lived in tin-roof shacks.
“We’ve had no water for three days now,” one resident of the capital city, Mamoudzou said. “Some of my neighbours are hungry and thirsty,” another one said.
Rescue workers, including reinforcements from France, are combing through the debris searching for survivors. The local prefect said the death toll could reach thousands.
Authorities said they were having difficulty establishing the number of deaths due to the large number of undocumented migrants – over 100,000 – in a population of 320,000.
Widespread damage to infrastructure – with downed power lines and impassable roads – is severely hindering emergency operations.
A first flight with supplies has arrived but there are severe shortages of food, water and shelter in certain areas.
Mamoudzou resident, John Balloz, said he was surprised he did not die when the cyclone struck.
“I was screaming because I could see the end coming for me,” he said.
“Everything is damaged, nearly everything, the water treatment plant, electric pylons, there’s a lot to do.
“There’s nothing much people can do, people are keeping still, they haven’t moved, they are waiting for help, help for food, for the electricity to be back up, and water also, there’s no running water.”
Mohamed Ishmael, who also lives in the capital, told Reuters news agency the situation there was “a tragedy” and said: “You feel like you are in the aftermath of a nuclear war… I saw an entire neighbourhood disappear.”
“It’s the hunger that worries me most,” Mayotte Senator Salama Ramia told French media. “There are people who have had nothing to eat or drink” since Saturday, she said.
 Reuters
ReutersFrancois-Xavier Bieuville, the island’s prefect, told local media the death toll could rise significantly once the damage was fully assessed. He warned it would “definitely be several hundred” and could reach the thousands.
Mayotte’s impoverished communities, including undocumented migrants who have travelled to the French territory in an effort to claim asylum, are thought to have been particularly hard hit due to the vulnerable nature of their housing.
The Muslim tradition of burying the dead within 24 hours also meant documenting the number of those who have perished was more difficult, the prefect said.
In addition to aid, 110 French soldiers have arrived to help with the rescue, with another 160 on the way.
French Interior Minister Bruno Retailleau is scheduled to visit the island to assess the damage and co-ordinate further relief efforts.
France colonised Mayotte in 1841 – and by the turn of the 20th Century added the three main islands that constitute the Comoros archipelago to its overseas territories.
Those there voted to become independent in 1974, but Mayotte decided to stay as part of France.
The island’s population is heavily dependent on French financial aid and has long struggled with poverty, unemployment and political instability.
About 75% of the population live below the national poverty line and unemployment hovers at around one in three.
 Getty Images
Getty Images
Cyclone Chido also made landfall in Mozambique, where it brought flash flooding, uprooted trees and damaged buildings about 25 miles (40km) south of the northern city of Pemba. Three deaths have been reported.
The cyclone caused structural damage and power outages in the northern coastal provinces of Nampula and Cabo Delgado on Saturday morning, local authorities reported.
Guy Taylor, a spokesperson for aid agency Unicef in Mozambique, said, “we were hit very hard in the early hours of this morning”.
“Many houses were destroyed or seriously damaged, and healthcare facilities and schools are out of action,” he added.
Mr Taylor said Unicef was concerned about “loss of access to critical services”, including medical treatment, clean water and sanitation, and also “the spread of diseases like cholera and malaria”.
Chido is the latest deadly storm whose intensity is being ascribed by many to climate change.
The “exceptional” cyclone was super-charged by particularly warm Indian Ocean waters, meteorologist Francois Gourand of the Meteo France weather service told AFP.




