Last updated:
 Why Trust Cryptonews
Why Trust Cryptonews
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and its central bank partners have successfully completed the testing phase of their Mandala project.
This collaborative initiative, involving the Reserve Bank of Australia, the Bank of Korea, Bank Negara Malaysia, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore, aims to streamline cross-border transactions by automating compliance procedures within a decentralized network.
Mandala Reaches Proof-of-Concept
On Oct. 28, the BIS announced that Mandala, a key BIS project for 2024, has successfully completed its proof-of-concept phase.
The project has been tested in two real-world scenarios.
The first scenario involved a cross-border lending transaction between Singapore and Malaysia. In this case, Mandala streamlined compliance processes for capital flow management (CFM) and sanctions screening for financial institutions. Additionally, it enabled real-time monitoring of compliance by central banks.
The second scenario focused on a cross-border capital investment financing transaction between South Korea and Australia. Here, Mandala automated sanctions screening and CFM reporting requirements for an unlisted securities transaction.
A Compliance-by-Design Approach
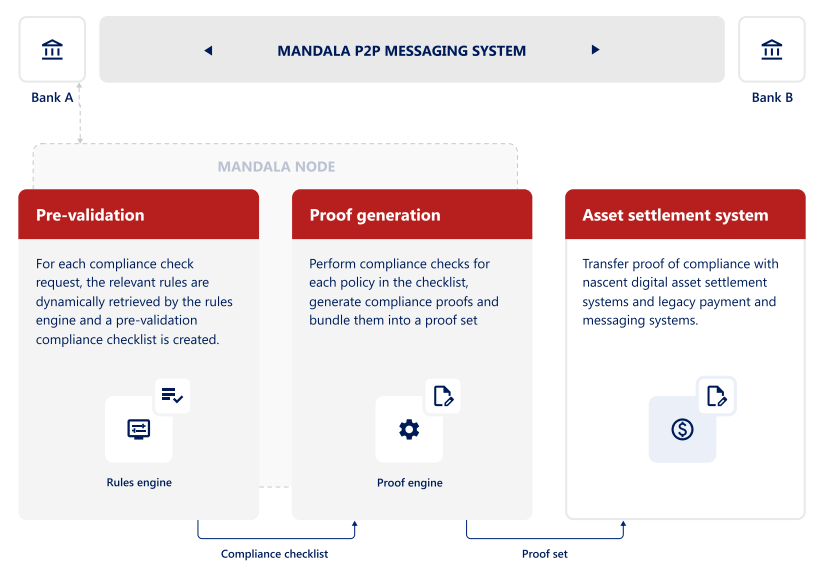
Mandala operates as a decentralized network, composed of interconnected nodes operated by participating institutions such as commercial and central banks. Each node comprises three key components: a peer-to-peer (P2P) messaging system, a rules engine, and a proof engine.
This network structure enables direct and secure communication between participants, eliminating the need for intermediaries. While adhering to existing regulations, Mandala incorporates jurisdiction-specific requirements like sanctions screening and capital flow management (CFM) measures into its system.
In addition, the system automatically generates cryptographic proofs of compliance to ensure compliance before funds are released.
To maintain privacy, Mandala also employs zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs. These cryptographic techniques allow a party to prove the validity of a claim without revealing sensitive information.
Integrating With Digital Assets and TradFi Systems
According to the BIS, Mandala can be used with traditional payment systems, such as Swift, as well as various digital assets, including central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), regulated stablecoins and other tokenized assets.
To facilitate cross-border transactions, Mandala uses a policy wrapper contract. This contract locks the original digital asset (for example, a CBDC) and mints a wrapped version. The wrapped asset can then be transferred between parties, with the transfer subject to specific compliance requirements.
These requirements are verified through cryptographic proofs, which are checked by smart contracts. By performing most compliance checks off-chain, Mandala ensures data privacy and reduces transaction costs.
More Efficient Global Financial System
The BIS added in its announcement that the Mandala project is purely experimental and does not imply any intention on the part of any participating commercial or central bank to adopt the Mandala system.
However, the BIS says it is providing valuable insights into the future of cross-border compliance and programmable compliance. The project’s success in automating compliance procedures, increasing efficiency and enhancing privacy shows its potential to improve international financial transactions, according to the BIS.
“In the long term, Mandala’s approach could enable seamless interoperability across regional payment systems, contributing to a more unified and efficient global financial market infrastructure.”