 BBC
BBCThe planet has moved a major step closer to warming more than 1.5C, new data shows, despite world leaders vowing a decade ago they would try to avoid this.
The European Copernicus climate service, one of the main global data providers, said on Friday that 2024 was the first calendar year to pass the symbolic threshold, as well as the world’s hottest on record.
This does not mean the international 1.5C target has been broken, because that refers to a long-term average over decades, but does bring us nearer to doing so as fossil fuel emissions continue to heat the atmosphere.
Last week UN chief António Guterres described the recent run of temperature records as “climate breakdown”.
“We must exit this road to ruin – and we have no time to lose,” he said in his New Year message, calling for countries to slash emissions of planet-warming gases in 2025.
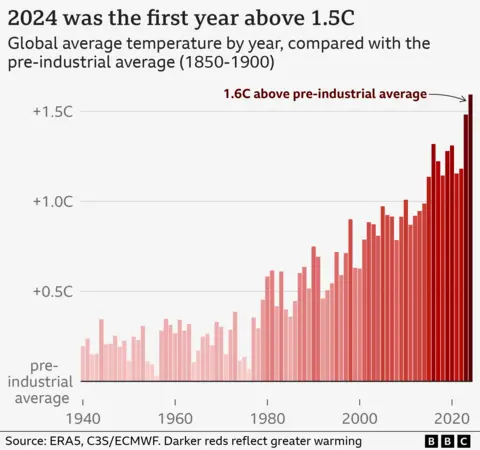
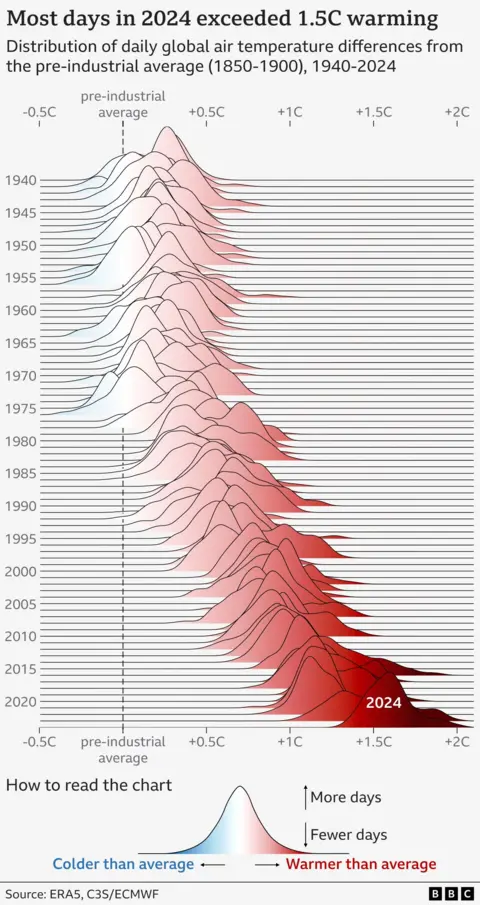
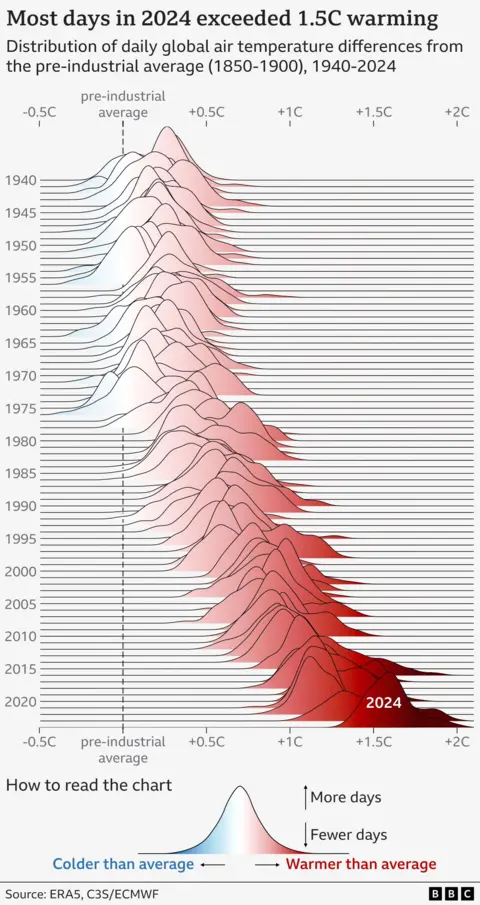
Global average temperatures for 2024 were around 1.6C above those of the pre-industrial period – the time before humans started burning large amounts of fossil fuels – according to Copernicus data.
This breaks the record set in 2023 by just over 0.1C, and means the last 10 years are now the 10 warmest years on record.
The Met Office, Nasa and other climate groups are due to release their own data later on Friday. All are expected to agree that 2024 was the warmest on record, although precise figures vary slightly.
Last year’s heat is predominantly due to humanity’s emissions of planet-warming gases, such as carbon dioxide, which are still at record highs.
Natural weather patterns such as El Niño – where surface waters in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean become unusually warm – played a smaller role.
“By far and away the largest contribution impacting our climate is greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere,” Samantha Burgess, deputy director of Copernicus, tells the BBC.
The 1.5C figure has become a powerful symbol in international climate negotiations ever since it was agreed in Paris in 2015, with many of the most vulnerable countries considering it a matter of survival.
The risks from climate change, such as intense heatwaves, rising sea-levels and loss of wildlife, would be much higher at 2C of warming than at 1.5C, according to a landmark UN report from 2018.
Yet the world has been moving closer and closer to breaching the 1.5C barrier.
“When exactly we will cross the long-term 1.5C threshold is hard to predict, but we’re obviously very close now,” says Myles Allen of the Department of Physics at the University of Oxford, and an author of the UN report.
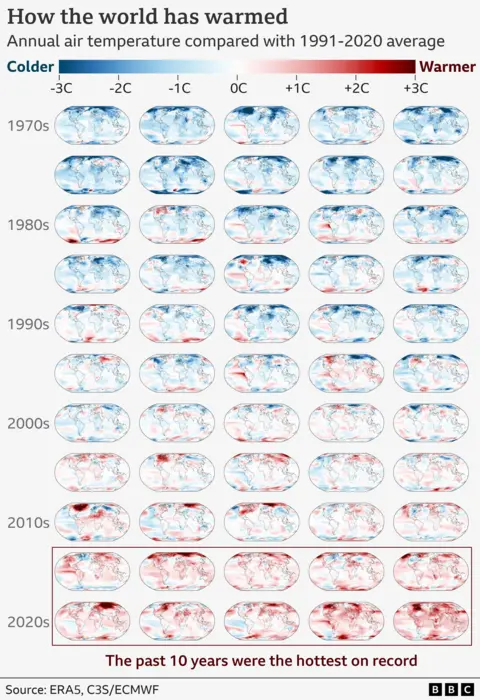
The current trajectory would likely see the world pass 1.5C of long-term warming by the early 2030s. This would be politically significant, but it wouldn’t mean game over for climate action.
“It’s not like 1.49C is fine, and 1.51C is the apocalypse – every tenth of a degree matters and climate impacts get progressively worse the more warming we have,” explains Zeke Hausfather, a climate scientist at Berkeley Earth, a research group in the US.
Even fractions of a degree of global warming can bring more frequent and intense extreme weather, such as heatwaves and heavy rainfall.
In 2024, the world saw blistering temperatures in west Africa, prolonged drought in parts of South America, intense rainfall in central Europe and some particularly strong tropical storms hitting north America and south Asia.
These events were just some of those made more intense by climate change over the last year, according to the World Weather Attribution group.
Even this week, as the new figures are released, Los Angeles has been overwhelmed with destructive wildfires fuelled by high winds and a lack of rain.
While there are many contributing factors to this week’s events, experts say conditions conducive to fires in California are becoming more likely in a warming world.
It wasn’t only air temperatures that set new marks in 2024. The world’s sea surface also reached a new daily high, while the total amount of moisture in the atmosphere reached record levels.
That the world is breaking new records is not a surprise: 2024 was always expected to be hot, because of the effect of the El Niño weather pattern – which ended around April last year – on top of human-caused warming.
But the margin of several records in recent years has been less expected, with some scientists fearing it could represent an acceleration of warming.
“I think it’s safe to say that both 2023 and 2024 temperatures surprised most climate scientists – we didn’t think we’d be seeing a year above 1.5C this early,” says Dr Hausfather.
“Since 2023 we’ve had around 0.2C of extra warming that we can’t fully explain, on top of what we had expected from climate change and El Niño,” agrees Helge Gößling, a climate physicist at the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany
Various theories have been suggested to explain this ‘extra’ warmth, such as an apparent reduction in the low-level cloud cover that tends to cool the planet, and prolonged ocean heat following the end of El Niño.
“The question is whether this acceleration is something persistent linked to human activities that means we will have steeper warming in the future, or whether it is a part of natural variability,” Dr Gößling adds.
“At the moment it’s very hard to say.”
Despite this uncertainty, scientists stress that humans still have control over the future climate, and sharp reductions in emissions can lessen the consequences of warming.
“Even if 1.5 degrees is out the window, we still can probably limit warming to 1.6C, 1.7C or 1.8C this century,” says Dr Hausfather.
“That’s going to be far, far better than if we keep burning coal, oil and gas unabated and end up at 3C or 4C – it still really matters.”